| Table of Contents | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
...
| Info |
|---|
Important
|
...
Download the SwarmFS package from the Downloads section on the DataCore Support Portal.
Install the EPEL release, which has the needed packages for NFS:
Code Block language bash yum -y install epel-release
Some later EPEL releases are missing the needed Ganesha and Ganesha utility packages, so install those:
Navigate to the NFS community build service.
Scroll down to the RPMs list and download both packages:
nfs-ganesha-<version>.rpm
nfs-ganesha-utils-<version>.rpm
Install both packages:
Code Block language bash yum -y install nfs-ganesha-<version>.rpm yum -y install nfs-ganesha-utils-<version>.rpm
Install the Swarm RPMs:
Code Block language bash yum install caringo-nfs-libs-<version>.rpm yum install caringo-nfs-<version>.rpm
Run the SwarmFS configuration shell script that generates the local SwarmFS service configuration, validates the environment, enables the SwarmFS services, and then starts the SwarmFS services.
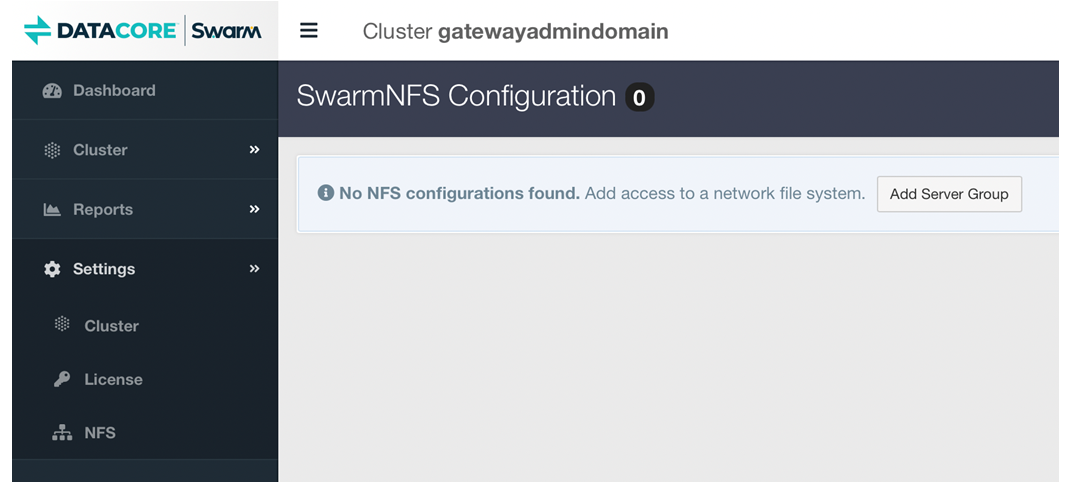
Login to Swarm UI, and navigate to Settings → NFS.
Click Add Server Group to create a new NFS Exports Group.
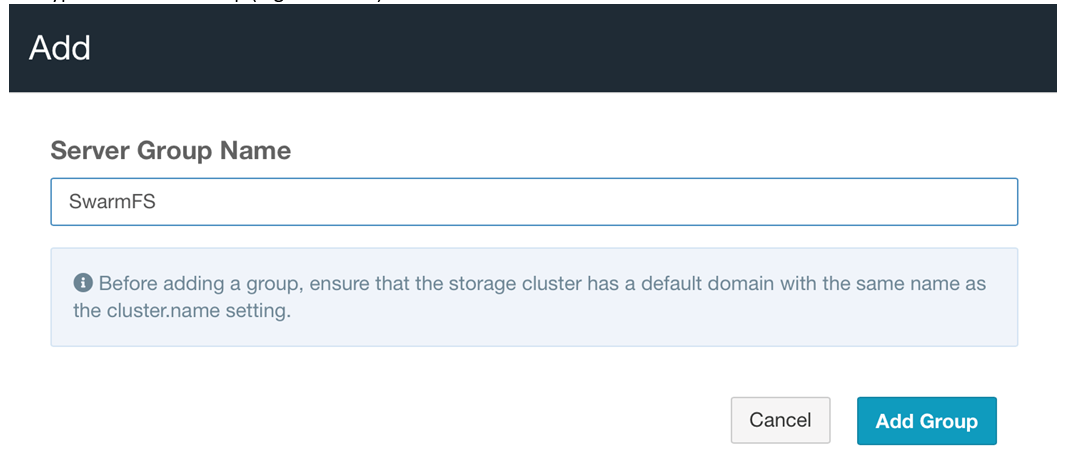
Provide the name of the group (e.g., SwarmFS) and click Add Group.
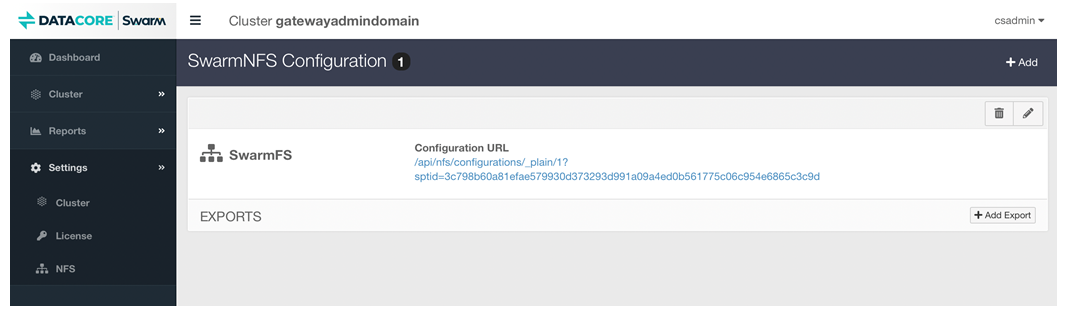
Click the link of the newly created NFS Export Group, to open a new window or tab.
The opened window or tab shows export configure (in JSON format), copy the URL.
Run the script.
SwarmNFS-ConfigOpen the SwarmNFS-Config wizard.
[root@swarmfs32-01 ~]# SwarmNFS-configPaste the URL “http://{gateway_ip}:91/api/nfs/configurations/_plain/1?sptid=244ee2c5072d9f0888a13d31d007c6cf37121369ca35636a4b4486c82e1e1e3a”.
Update the URL of nfs-ganesha configuration (/etc/ganesha/ganesha.caringo.conf) with credentials followed by @.
Configuration="http://dcadmin:datacore@{gateway_ip}:91/api/nfs/configurations/_plain/1?sptid=244ee2c5072d9f0888a13d31d007c6cf37121369ca35636a4b4486c82e1e1e3a "
Here the credentials are:username - dcadmin
password - datacore
Restart nfs-ganesha service.
systemctl restart nfs-ganesha
Enable the service to allow SwarmFS to start automatically on boot:
Code Block language bash systemctl enable /usr/lib/systemd/system/nfs-ganesha.service
Run this command to verify the status of the services:
Code Block language bash systemctl status nfs-ganesha
This status report is comprehensive and includes which processes are running.
...